|
|
|
 T This issue contains articles on energy-saving tips from energy.gov. We are including s imple and inexpensive actions that can help you save energy and money during these cold winter months. Visit the Website for these and more energy-saving tips. We hope you enjoy the newsletter and invite your comments and feedback. Also, we urge you to notify us of any changes in your email or mailing address. Just click on the " Comments & Feedback" link under "Quick Links" on the left. Thank you. |
 |
|
Air Sealing Your Home
Published November 26, 2013
|
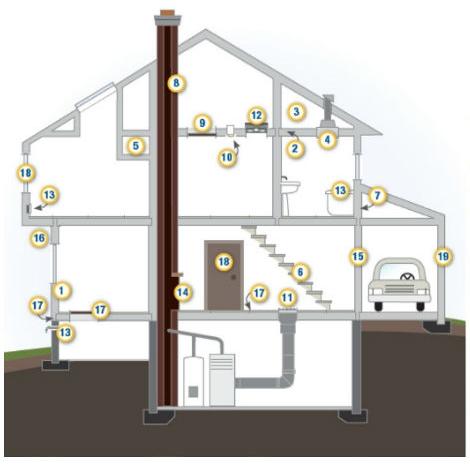
1. Air Barrier and Thermal Barrier Alignment, 2. Attic Air Sealing, 3. Attic Kneewalls, 4. Shaft for Piping or Ducts, 5. Dropped Ceiling/Soffit, Staircase Framing at Exterior Wall, 7. Porch Roof, 8. Flue or Chimney Shaft, 9. Attic Access, 10. Recessed Lighting, 11. Ducts, 12. Whole-House Fan, 13. Exterior Wall Penetrations, 14. Fireplace Wall, 15. Garage/Living Space Walls, 16. Cantilevered Floor, 17. Rim Joists, Sill Plate, Foundation, Floor, 18. Windows & Doors, 19. Common Walls Between Attached Dwelling Units.
|
Reducing the amount of air that leaks in and out of your home is a cost-effective way to cut heating and cooling costs, improve durability, increase comfort, and create a healthier indoor environment. Caulking and weatherstripping are two simple and effective air-sealing techniques that offer quick returns on investment, often one year or less. Caulk is generally used for cracks and openings between stationary house components such as around door and window frames, and weatherstripping is used to seal components that move, such as doors and operable windows.
AIR LEAKAGE Air leakage occurs when outside air enters and conditioned air leaves your house uncontrollably through cracks and openings. It is unwise to rely on air leakage for ventilation. During cold or windy weather, too much air may enter the house. When it's warmer and less windy, not enough air may enter, which can result in poor indoor air quality. Air leakage also contributes to moisture problems that can affect occupants' health and the structure's durability. An added benefit is that sealing cracks and openings reduces drafts and cold spots, improving comfort.
The recommended strategy is to reduce air leakage as much as possible and to provide controlled ventilation as needed. Before air sealing, you should first:
- Detect air leaks
- Assess your ventilation needs for indoor air quality.
You can then apply air sealing techniques and materials, including caulk and weatherstripping. If you're planning an extensive remodel of your home that will include some construction, review some of the techniques used for air sealing in new home construction and consider a home energy audit to identify all the ways your home wastes energy and money. Note that air sealing alone doesn't eliminate the need for proper insulation to reduce heat flow through the building envelope.
|
 |
Where to Insulate in a HomePublished November 26, 2013 Energysaver.gov
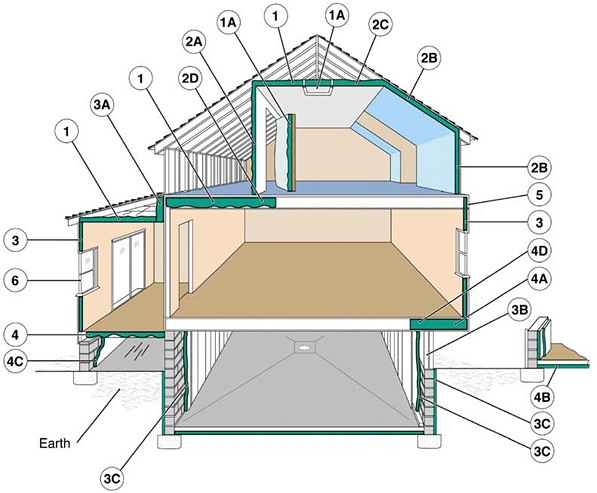 |
Examples of where to insulate. 1. In unfinished attic spaces, insulate between and over the floor joists to seal off living spaces below. (1A) attic access door 2. In finished attic rooms with or without dormer, insulate (2A) between the studs of "knee" walls, (2B) between the studs and rafters of exterior walls and roof, (2C) and ceilings with cold spaces above. (2D) Extend insulation into joist space to reduce air flows. 3. All exterior walls, including (3A) walls between living spaces and unheated garages, shed roofs, or storage areas; (3B) foundation walls above ground level; (3C) foundation walls in heated basements, full wall either interior or exterior. 4. Floors above cold spaces, such as vented crawl spaces and unheated garages. Also insulate (4A) any portion of the floor in a room that is cantilevered beyond the exterior wall below; (4B) slab floors built directly on the ground; (4C) as an alternative to floor insulation, foundation walls of unvented crawl spaces. (4D) Extend insulation into joist space to reduce air flows. 5. Band joists. 6. Replacement or storm windows and caulk and seal around all windows and doors. Source: Oak Ridge National Laboratory
|
For optimal energy efficiency, your home should be properly insulated from the roof down to its foundation. In addition to insulation, consider moisture and air leakage control in each area of your house. If radon is an issue where you live, you'll also need to consider radon and radon-resistant construction techniques as you research foundation insulation options. In addition, if you live in an area with termites, you'll have to consider how termite protection will affect the choice and placement of insulation in your home.
ATTIC INSULATION
Loose-fill or batt insulation is typically installed in an attic. Loose-fill insulation is usually less expensive to install than batt insulation, and provides better coverage when installed properly. See more on different types of insulation. Before insulating, seal any air leaks and make roof and other necessary repairs. If it is located in a conditioned part of the house, also remember to insulate and air seal your attic access.
Insulate and air seal any knee walls -- vertical walls with attic space directly behind them -- in your home as well. In addition, if you're building a new home or remodeling, make sure any attic decking that provides additional storage space or a platform for a heating and/or cooling unit or hot water tank is raised above the ceiling joists to leave room for adequate insulation. Finally, if you live in a hot or warm climate, consider installing a radiant barrierin your attic to reduce summer heat gain.
DUCT INSULATION
If the ducts in your home are in unconditioned space, seal and insulate them. If you're building a new house, place ducts in the conditioned space to avoid the energy losses associated with most duct systems.
Read more.
|
 |
|
Renew Memberships Online
At the request of our members, RAUS is pleased to provide the ability to renew their membership online and pay by credit or debit card. Just go to our website at www.raushome.com and click on the Online Dues Renewal button. If you are considering converting to a Lifetime Membership, click on the Membership button and select Life Membership.
 
|

|

Thermostats
Published November 26, 2013
Energysaver.gov
You can save money on your heating and cooling bills by simply resetting your thermostat when you are asleep or away from home. You can do this automatically without sacrificing comfort by installing an automatic setback or programmable thermostat.
Using a programmable thermostat, you can adjust the times you turn on the heating or air-conditioning according to a pre-set schedule. Programmable thermostats can store and repeat multiple daily settings (six or more temperature settings a day) that you can manually override without affecting the rest of the daily or weekly program. GENERAL THERMOSTAT OPERATION
You can easily save energy in the winter by setting the thermostat to 68°F while you're awake and setting it lower while you're asleep or away from home. By turning your thermostat back 10° to 15° for 8 hours, you can save 5% to 15% a year on your heating bill -- a savings of as much as 1% for each degree if the setback period is eight hours long. The percentage of savings from setback is greater for buildings in milder climates than for those in more severe climates. In the summer, you can follow the same strategy with central air conditioning by keeping your house warmer than normal when you are away, and lowering the thermostat setting to 78°F (26°C) only when you are at home and need cooling. Although thermostats can be adjusted manually, programmable thermostats will avoid any discomfort by returning temperatures to normal before you wake or return home. A common misconception associated with thermostats is that a furnace works harder than normal to warm the space back to a comfortable temperature after the thermostat has been set back, resulting in little or no savings. In fact, as soon as your house drops below its normal temperature, it will lose energy to the surrounding environment more slowly. The lower the interior temperature, the slower the heat loss. So the longer your house remains at the lower temperature, the more energy you save, because your house has lost less energy than it would have at the higher temperature. The same concept applies to raising your thermostat setting in the summer -- a higher interior temperature will slow the flow of heat into your house, saving energy on air conditioning. Check out our home heating infographic to learn more about how heating systems and thermostats interact. LIMITATIONS FOR HOMES WITH HEAT PUMPS, ELECTRIC RESISTANCE HEATING, STEAM HEAT, AND RADIANT FLOOR HEATING
Programmable thermostats are generally not recommended for heat pumps. In its cooling mode, a heat pump operates like an air conditioner, so turning up the thermostat (either manually or with a programmable thermostat) will save energy and money. But when a heat pump is in its heating mode, setting back its thermostat can cause the unit to operate inefficiently, thereby canceling out any savings achieved by lowering the temperature setting. Maintaining a moderate setting is the most cost-effective practice. Recently, however, some companies have begun selling specially designed programmable thermostats for heat pumps, which make setting back the thermostat cost-effective. These thermostats typically use special algorithms to minimize the use of backup electric resistance heat systems.
Electric resistance systems, such as electric baseboard heating, require thermostats capable of directly controlling 120-volt or 240-volt circuits. Only a few companies manufacture line-voltage programmable thermostats. The slow response time -- up to several hours -- of steam heating and radiant floor heating systems leads some people to suggest that setback is inappropriate for these systems. However, some manufacturers now offer thermostats that track the performance of your heating system to determine when to turn it on in order to achieve comfortable temperatures at your programmed time. Alternately, a normal programmable thermostat can be set to begin its cool down well before you leave or go to bed and return to its regular temperature two or three hours before you wake up or return home. This may require some guesswork at first, but with a little trial and error you can still save energy while maintaining a comfortable home.
|
 |
 Keep Us Accurate Keep Us Accurate
To be sure your benefits are properly recorded, please advise the association when you change your name or address. If you receive inaccurate membership cards or other correspondence, we want to know. We do not mind reissuing membership cards. |
 |
 Portable Heaters Portable Heaters
Published November 26, 2013
Energysaver.gov
Small space heaters are typically used when the main heating system is inadequate or when central heating is too costly to install or operate. In some cases, small space heaters can be less expensive to use if you only want to heat one room or supplement inadequate heating in one room. They can also boost the temperature of rooms used by individuals who are sensitive to cold, especially elderly persons, without overheating your entire home.
Space heater capacities generally range between 10,000 Btu and 40,000 Btu per hour, and commonly run on electricity, propane, natural gas, and kerosene (see wood and pellet heating for information on wood and pellet stoves).
Although most space heaters work by convection (the circulation of air in a room), some rely on radiant heating. Radiant heaters emit infrared radiation that directly heats objects and people within their line of sight, and are a more efficient choice when you will be in a room for only a few hours and can stay within the line of sight of the heater. They can also be more efficient when you will be using a room for a short period because they save energy by directly heating the occupant of the room and the occupant's immediate surroundings rather than the whole room. Safety is a top consideration when using space heaters. The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission estimates that more than 25,000 residential fires every year are associated with the use of space heaters, resulting in more than 300 deaths. In addition, an estimated 6,000 people receive hospital emergency room care for burn injuries associated with contacting the hot surfaces of room heaters, mostly in non-fire situations. When buying and installing a small space heater, follow these guidelines: - Only purchase newer model heaters that have all of the current safety features. Make sure the heater carries the Underwriter's Laboratory (UL) label.
- Choose a thermostatically controlled heater, because they avoid the energy waste of overheating a room.
- Select a heater of the proper size for the room you wish to heat. Do not purchase oversized heaters. Most heaters come with a general sizing table.
- Locate the heater on a level surface away from foot traffic. Be especially careful to keep children and pets away from the heater.
|
 |
 Identity Theft Protection Service For RAUS Members Identity Theft Protection Service For RAUS Members
AllClear ID is the technology leader in the identity protection and credit monitoring market. The patented identity protection technology developed by AllClear ID makes it simple for you to protect your identity, and easy to take action if your personal information is compromised. RAUS members will enjoy a 20% discount off the regular monthly rate.
Just go to our website at www.raushome.com and click on the Discounts button and select Technology & Security. From there, go to the AllClear ID login page and input the following Activation Code: "raus". This will allow you to register and receive the discounted rate. |
 |
|
Seasonal Flu Update From the CDC
 F Flu activity remains high overall but is declining in parts of the country while increasing in other parts of the country according to this week's FluView report. Most notably the Southeast, which began experiencing high levels of flu activity at the end of November, is now showing declines in activity. CDC continues to receive reports of flu-related hospitalizations and deaths. Flu activity is likely to continue for some time. Anyone aged 6 months and older who has not gotten a flu vaccine yet this season should get one now, especially if they are in a part of the country where activity is still at a high level. All flu vaccines are designed to protect against 2009 H1N1 viruses which are the most common flu viruses identified so far this season. It's also important that people with high risk conditions who develop flu-like symptoms or those with severe illness consult a health care provider to see whether influenza antiviral drugs might be needed.
|
 |
Membership Dues
| AGE RANGE | LIFE DUES | | 40 or less | $325 | | 41 to 45 | $300 | | 46 to 50 | $275 | | 51 to 55 | $250 | | 56 to 60 | $225 | | 61 to 65 | $200 | | 66 to 70 | $175 | | 70 and up | $100 |
 Annual dues are $10 per year. Discounts apply for multiple year memberships: 3 years for $25 and 5 years for $40. Like memberships are available based on the age of the member at the time of the Life conversion. A Life Membership is exempt of dues increase and covers both the member and the spouse. |
 |
About RAUS
We are a non-political military association organized in 1970 to secure quality benefits for our members at rates only available to groups. Qualified retired and active members of the United States armed forces and related departments may join.
Membership benefits include discounts and perks, self-help and financial calculators, time-savings and educational resources, along with TRICARE Supplement, CHAMPVA Supplement and other insurance products.
RAUS is partnering with other organizations to establish a long term win-win relationship based on mutual benefits and information available to military families.
For more information, visit our website at www.raushome.com.

RAUS Eligible Defense Departments
* AIR FORCE * ARMY * MARINES * NAVY * NATIONAL GUARD *
* COAST GUARD * NOAA * CIVIL AIR PATROL *
* PUBLIC HEALTH SERVICE * COASTAL & GEODETIC SURVEY *
* ACTIVE & RETIRED * OFFICERS & ENLISTED *

|
|
|
Sincerely,
DONALD T. RUCK, President Retired Association for the Uniformed Services, Inc. Back To Top |
|
|